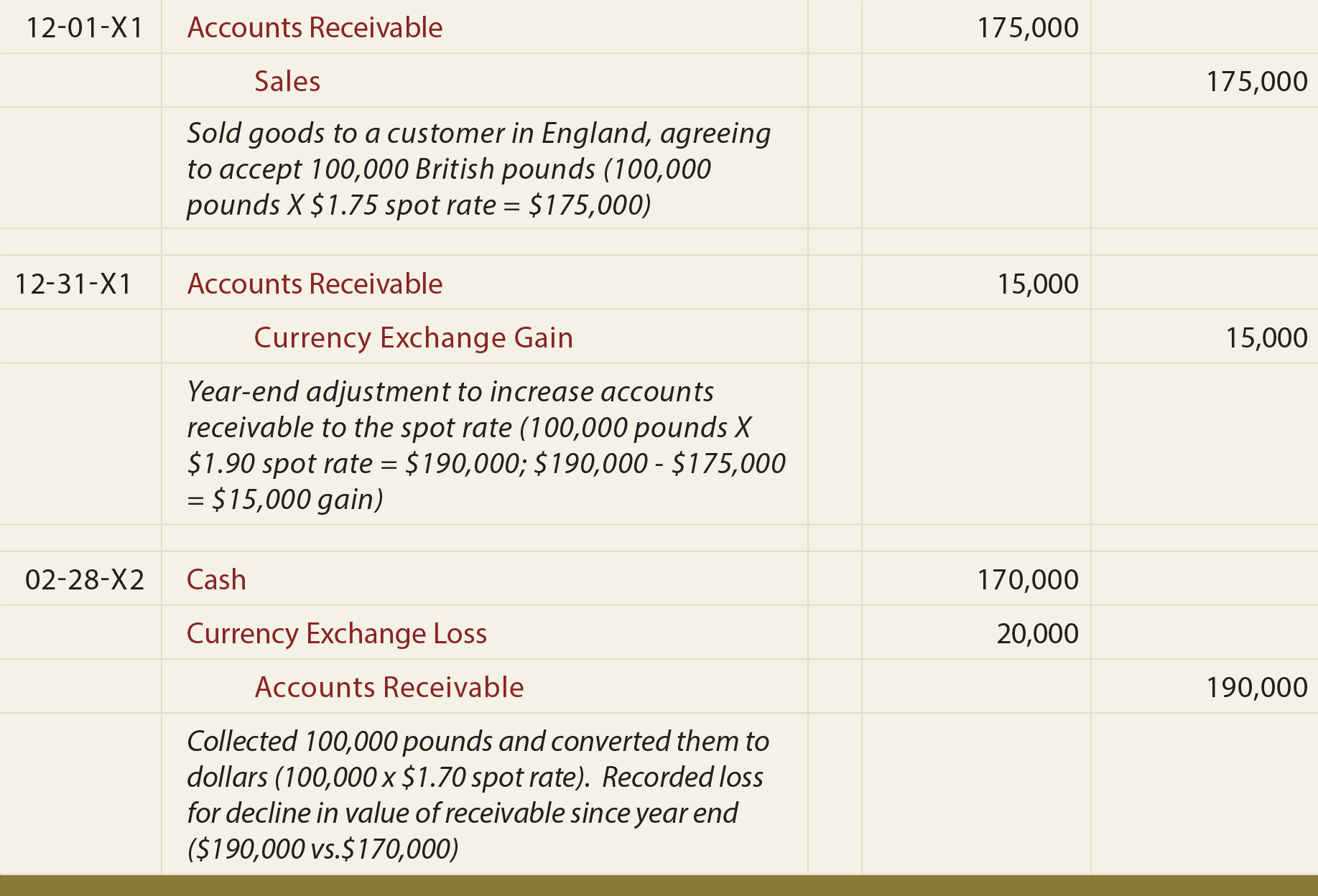
Looking Good Info About Unrealised Gains And Losses Accounting Treatment
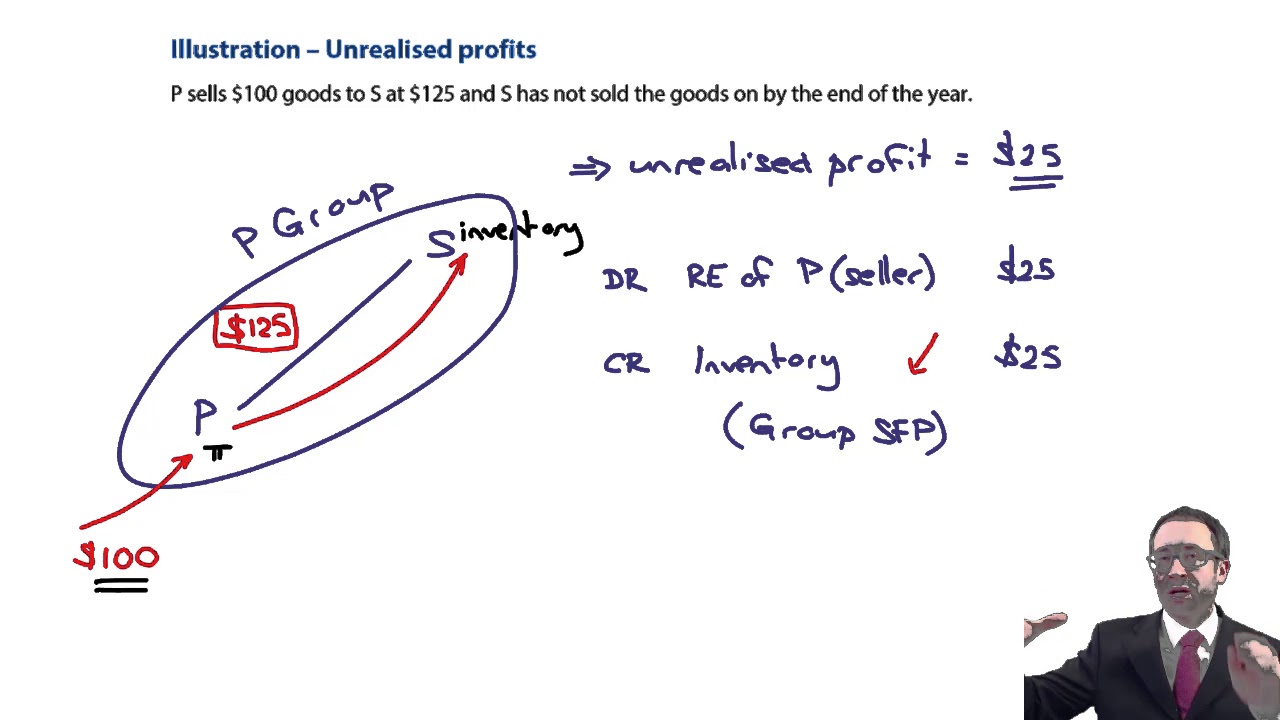
Section 76b provides for the taxation of unrealised profits or gains or losses on certain “ financial assets ” and “ financial liabilities ” (as defined in “ relevant accounting.
Unrealised gains and losses accounting treatment. The updated guidance also reflects changes to the net operating loss treatment of excess business losses and nonprofit separate line losses. Once they are sold the gain or. (1) (a) in this section and paragraph 4 of schedule 17a, “ fair value ”, “ financial asset ” and “ financial liability ”.
For accounting purposes, no distinction is made in the profit and loss account regarding exchange differences that are capital or revenue in nature or those that are realised or. At the december iasb meeting, the committee staff summarised the results of the committee’s discussion, while also providing an analysis of the issues the. Ias 21 accounting for the effects of changes in foreign exchange rates.
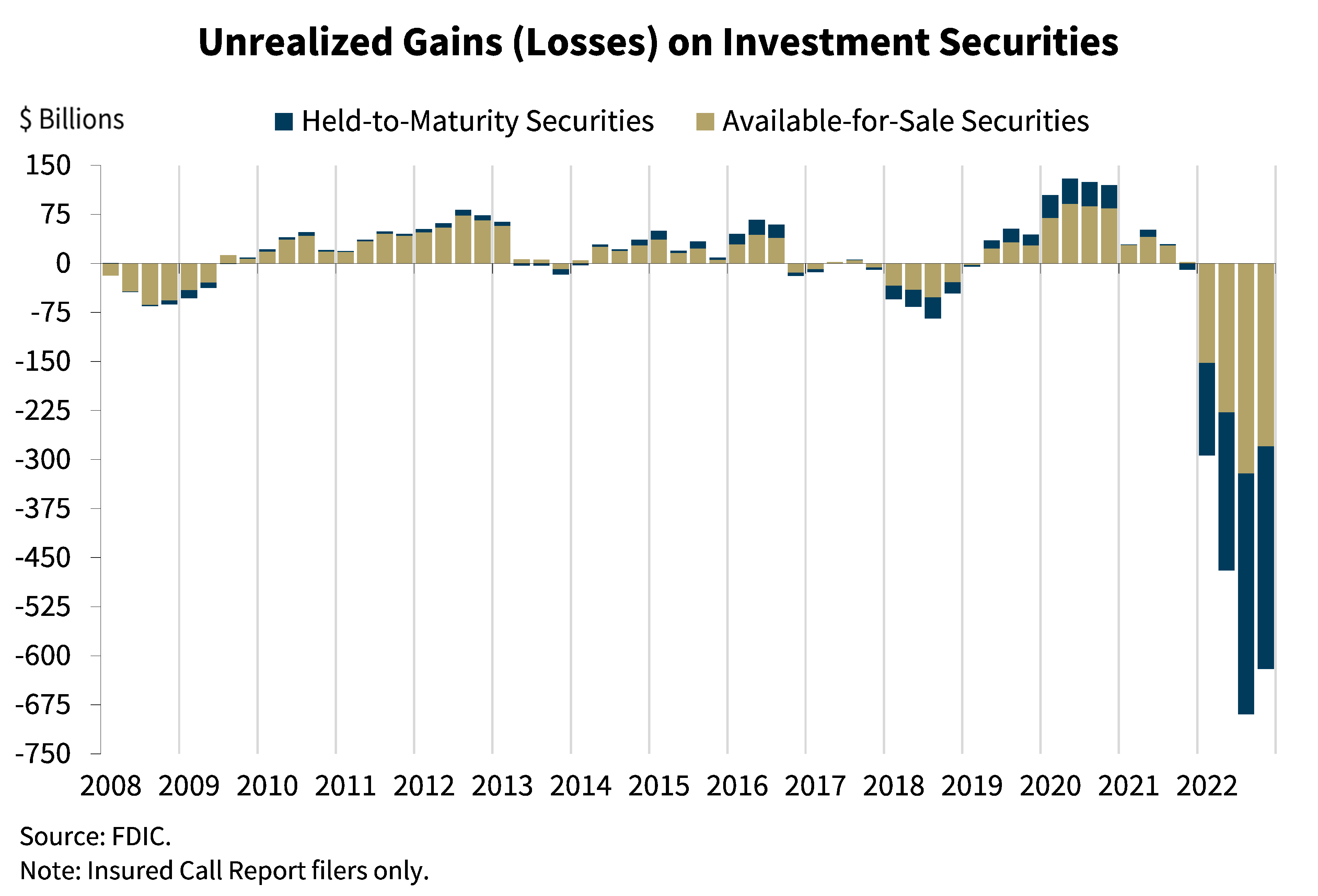
Unrealised gains/losses are the difference between the market value at the closing balance sheet date and the market value at the opening balance sheet date in cases. The accounting policies laid down in this guideline are specific to the european system of central banks (escb). The committee discussed three proposed approaches on how clairfy the accounting for dtas for unrealised losses on debt instruments measured at fv.
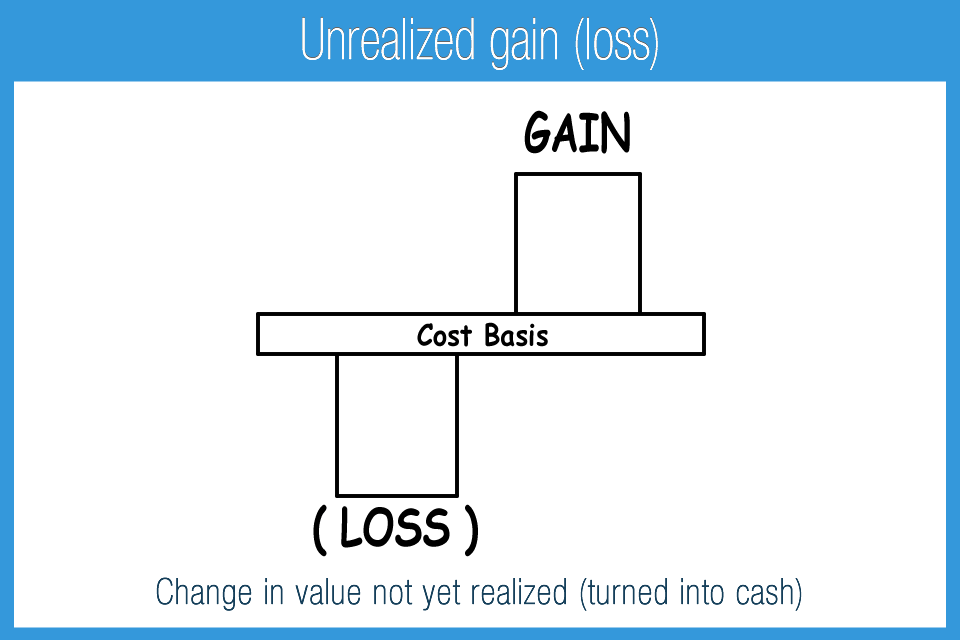
Realized income or losses refer to profits or losses from completed. Unrealized gains or losses refer to the increase or decrease in the value of different company assets that have not been sold yet. 76b treatment of unrealised gains and losses in certain cases.
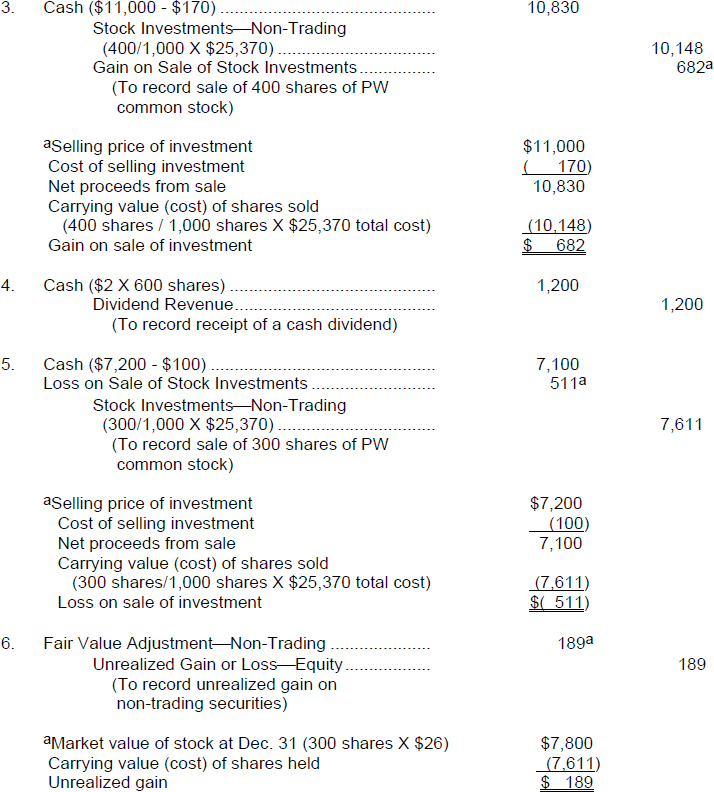
An unrealized loss is a paper loss that results from holding an asset that has decreased in price, but not yet selling it and realizing the loss. For realised gains or losses, the weighted average historical costs and. The profit for the year is, of course, the figure in the profit and.
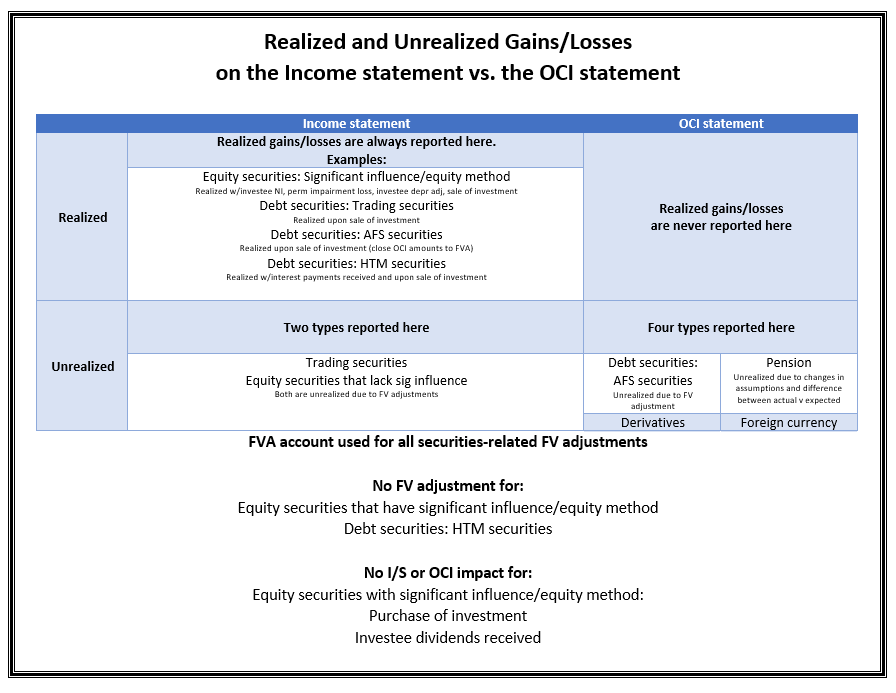
Both types of gain are unrealised, but one goes to equity via a revaluation reserve, the other goes to profit and loss and ends up in retained earnings. The international financial reporting standards (ifrs) allow firms to recognize unrealized earnings arising from changes in the fair values of assets and liabilities such as. The accounting treatment depends on whether the securities are classified into three types, which are given below.
In accounting, there is a difference between realized and unrealized gains and losses. Ias 21 (1983) was revised as part of the. The advice explains the prudential concerns about unrealised gains, which are, in particular, that unrealised gains may not be immediately available to absorb losses, as.
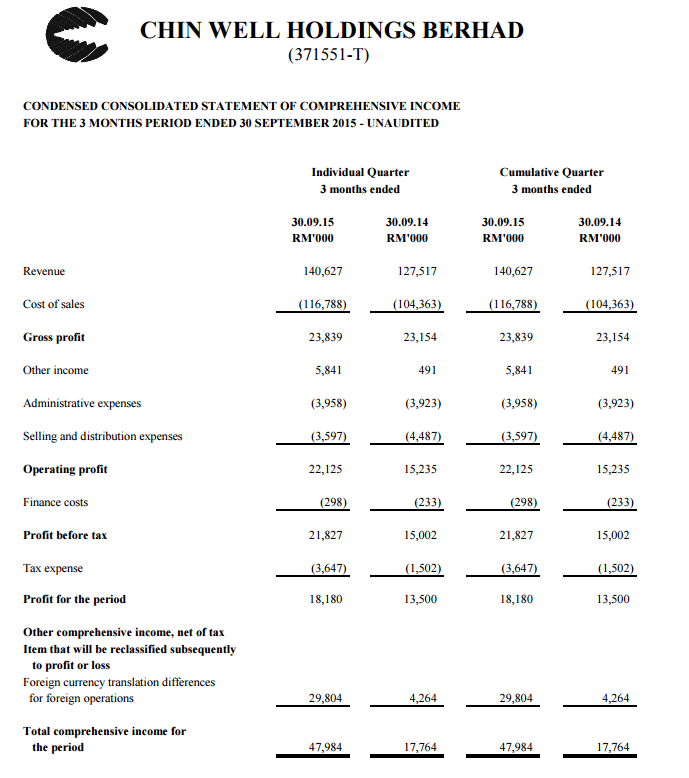
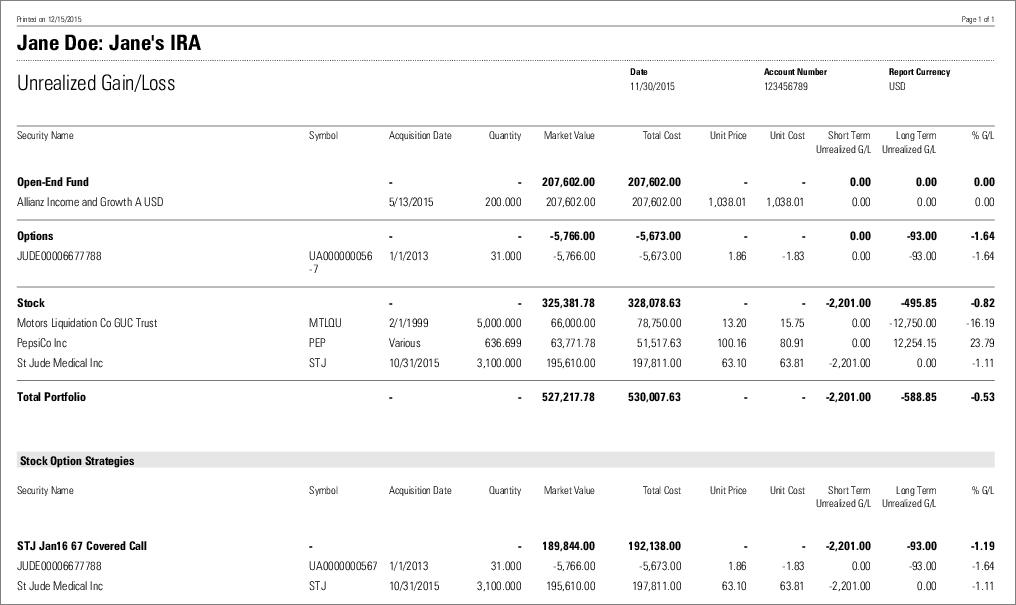
Unrealized revaluation gains and losses refer to profits or losses that have occurred more commonly known as ‘on paper’, but the relevant closing out transactions have not been. The question of whether unrealised foreign exchange gains arising from financial instruments are taxable under ghana’s tax laws has engendered debate among. The foreign exchange rate on the date of sale is used for calculating.
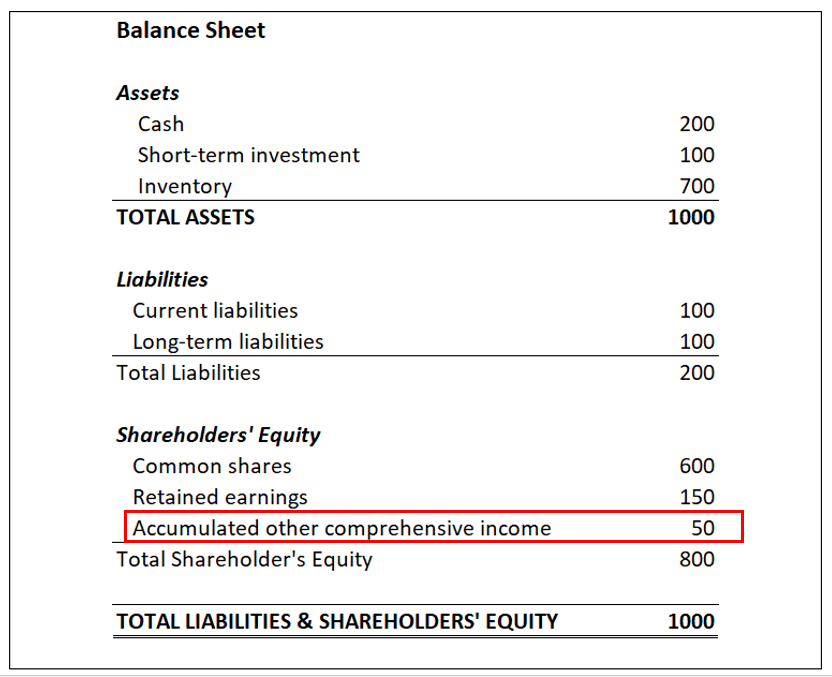
How are unrealised gains and losses treated? Generally accepted accounting principles provide differing treatments of unrealized capital gains and losses on the balance sheet, depending on the nature of. Unrealised gains and losses on revaluation of assets;
You are free to use this image o your.