Sensational Tips About Disclosure Of Contingent Liabilities In Financial Statements Business Balance Sheet Format

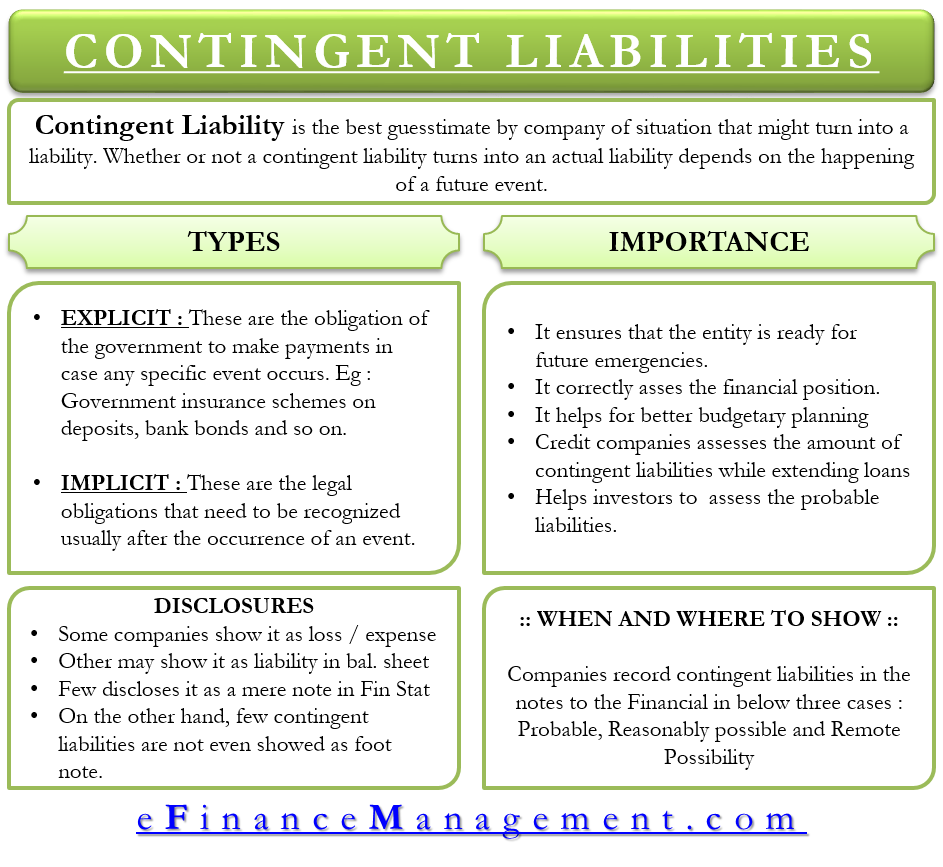
The problem of reporting contingent liabilities is the determination of the existence of possible contingent liabilities at the balance sheet date.
Disclosure of contingent liabilities in financial statements business balance sheet format. The liability may be a legal obligation or a constructive obligation. Contingent liabilities must be disclosed in the financial statements if there is a possible obligation that could result in expenditure, or a present obligation not recognized because it is not probable that an outflow of resources embodying economic benefits will be required to settle the obligation, or the amount of the obligation cannot be. Preparers may also consider practice statement 2 making materiality judgements, which provides guidance and examples on applying materiality in the preparation of financial statements.
First, it must be possible to estimate the value of the contingent liability. The recognition, measurement, classification or disclosure of an item or information in the financial statements is made relying on these estimates. Remote contingent liabilities are extremely.
Usfinancial statement presentation guide 1.1. Both gaap (generally accepted accounting principles) and ifrs (international financial reporting standards) require companies to record contingent liabilities, due to their connection with three important accounting principles. For example, assume a reporting entity includes balance sheets for two years and income statements for three years in its 20x3 financial statements.
The article discusses the importance of accurate representation of current and contingent liabilities in financial statements for stakeholders' understanding, outlines the difference between these two types of liabilities, and introduces ind as schedule iii as a guideline for accurate disclosure, followed by a suggestion of a checklist for compliance. The warranty is good for one year. It also requires the use of accounting estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the financial year.
A provision is a liability of uncertain timing or amount. This chapter introduces the general concepts of financial statement presentation and disclosure that underlie the detailed guidance that is covered in the remaining chapters of this guide. Those bonds are thus listed as liabilities on the company’s balance sheet.
Latest from taxmann. The auditing procedure for contingent liabilities is directed toward the detection of the items, and their possible future effect on operations and financial position. Updated may 22, 2022 reviewed by david kindness fact checked by ryan eichler a contingent liability is an existing condition or set of circumstances involving uncertainty regarding possible.
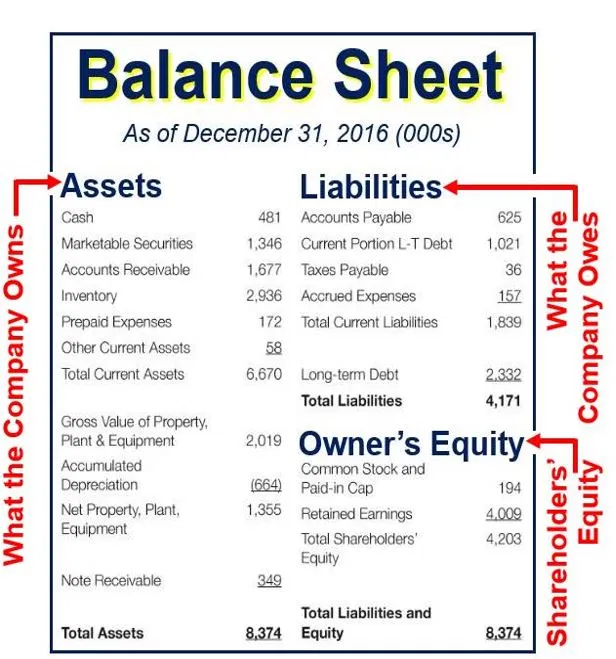
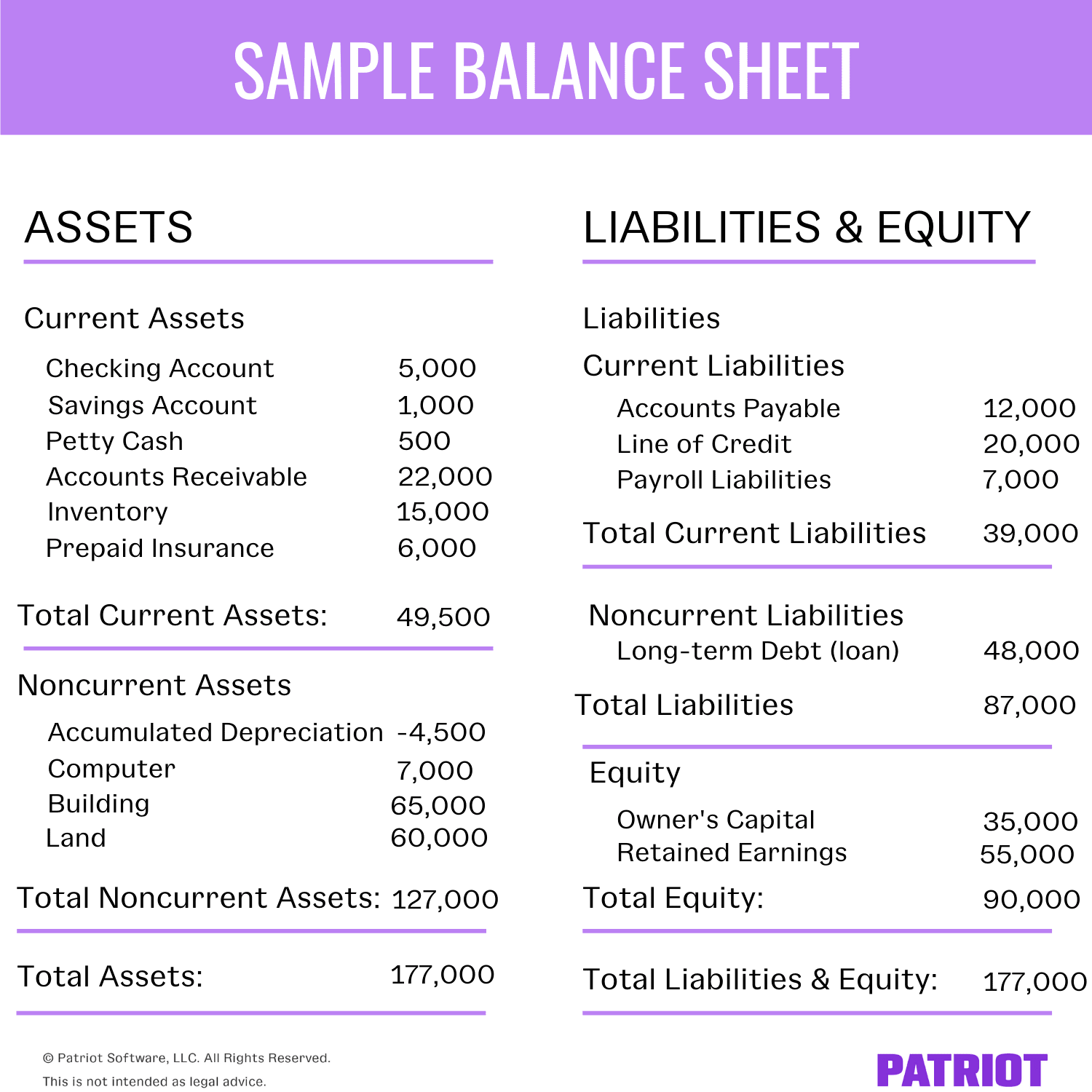
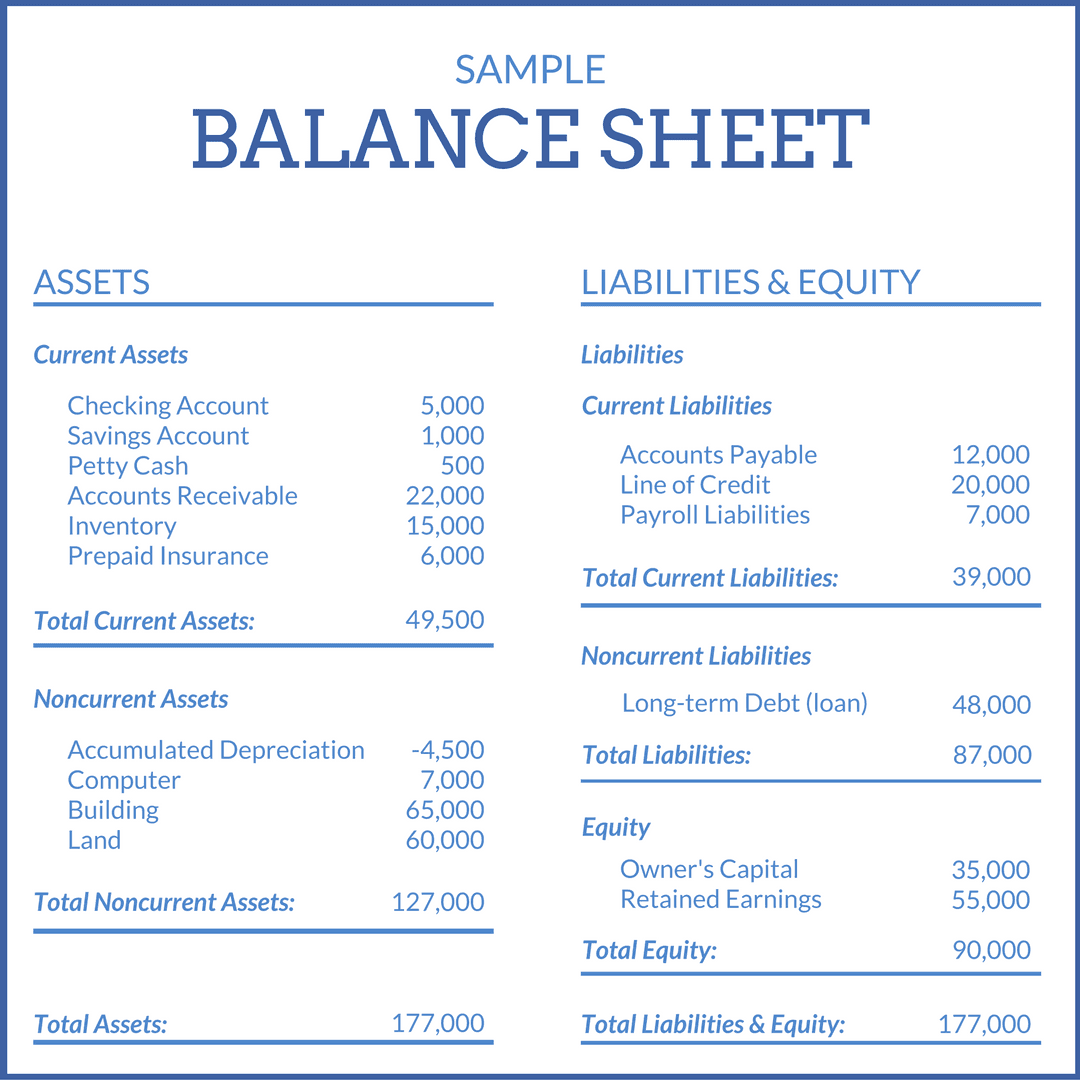
On a company’s balance sheet, owners’ equity shows what the owners of the business (or shareholders) would have if the company paid off all its debt with its assets. If it completed a material acquisition in 20x1, the reporting entity should disclose the 20x1 income statement disclosures in their 20x3 financial statements. A loss contingency that is probable or possible but the amount cannot be estimated means the amount cannot be recorded in the company's accounts or reported as liability on the balance sheet.
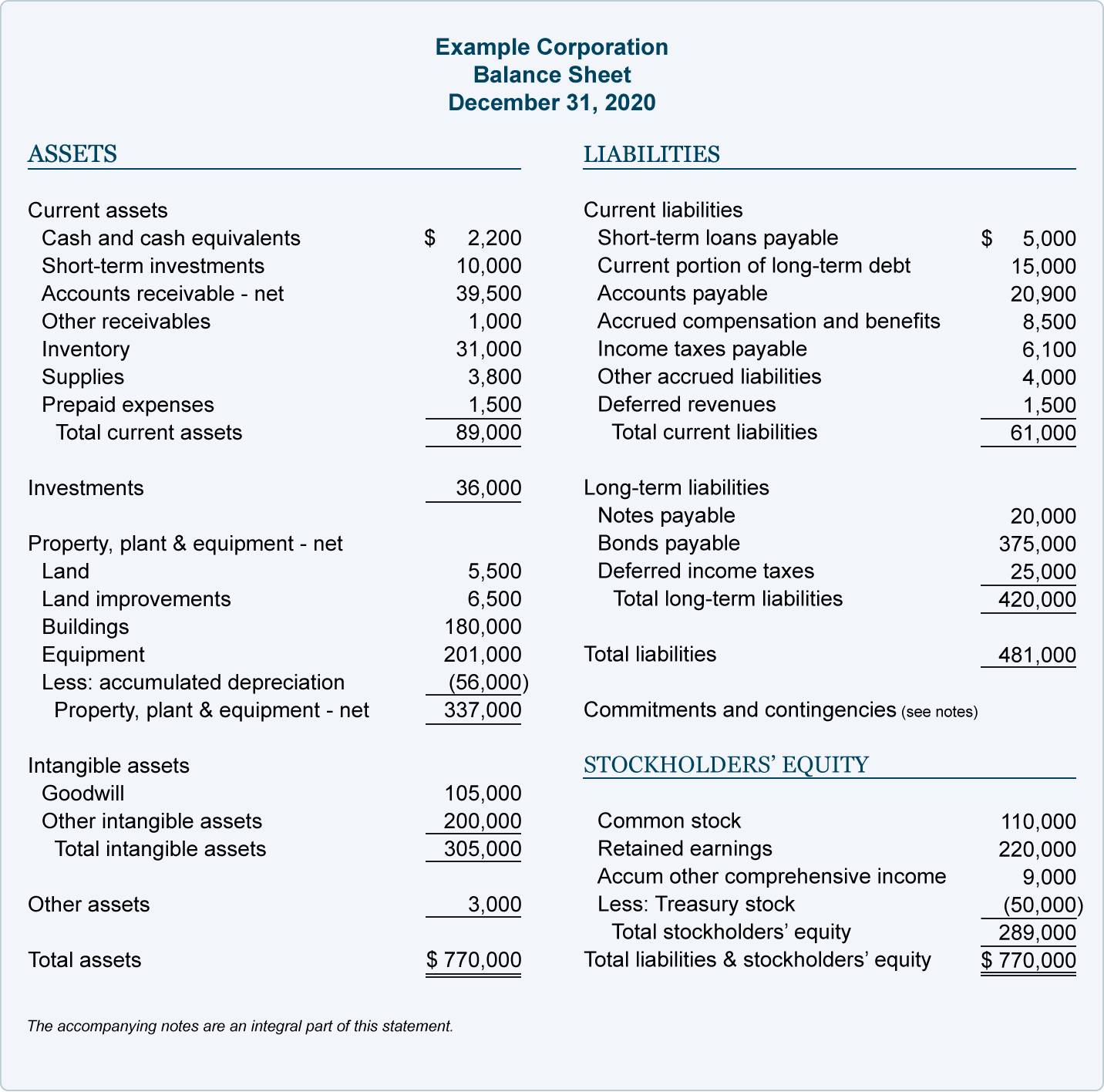
The proposed disclosure of contingent liabilities and commitments required registrants to disclose, either in text or in tabular format, the expected amount, range of amounts or maximum amount of contingent liabilities and commitments, aggregated by type and by time period of the expiration of the commitment. The possible contingent liability is disclosed in the financial statement footnotes and should not be reflected on the balance sheet, even though it is possible to estimate the possible amount of a loss. Preparers may also consider practice statement 2 making materiality judgements, which provides guidance and examples on applying materiality in the preparation of financial statements.
Contingent liabilities are recorded to ensure that the financial statements are accurate and meet requirements of generally accepted accounting principles (gaap) or international. Remember the balance sheet formula: Ias 37 defines and specifies the accounting for and disclosure of provisions, contingent liabilities, and contingent assets.
Contingent liabilities must pass two thresholds before they can be reported in financial statements. Reported amounts of assets and liabilities, disclosure of contingent liabilities as at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Following the generally accepted accounting principles, commitments are recorded when they occur, while contingencies (should they relate to a liability or future fund outflow) are at a minimum disclosed in the notes to the statement of financial position (balance sheet) in the financial statements of a business.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ScreenShot2022-04-26at10.45.59AM-aab9d8741c8f4ee1aff95f057ca2ab3a.png)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Balance_Sheet_Aug_2020-01-4cad5e9866c247f2b165c4d9d4f7afb7.jpg)