Fine Beautiful Info About Unrealised Profit Journal Entry
An unrealized gain is an increase in the value of an asset that has not been sold.
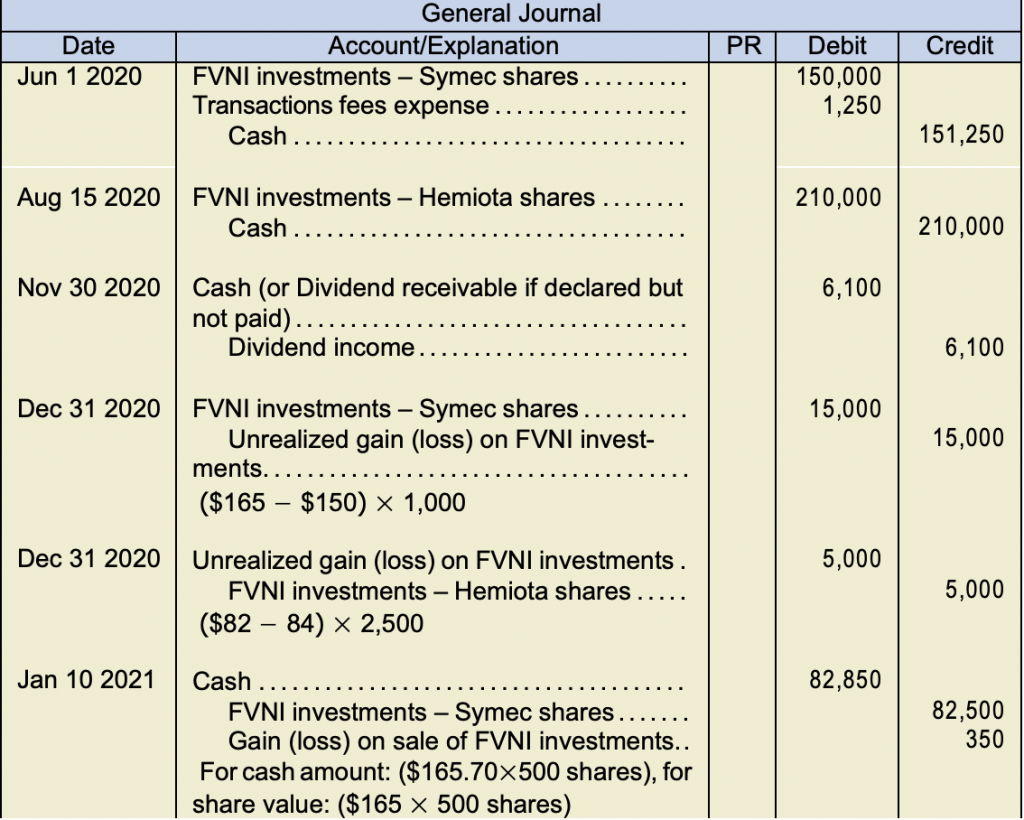
Unrealised profit journal entry. As only half of the. What are unrealized gains/losses? The international financial reporting standards (ifrs) allow firms to recognize unrealized earnings arising from changes in the fair values of assets and liabilities such as.
Journal entry for unrealized gain. Unrealized gains or losses refer to the increase or decrease in the paper value of the different assets of the company which have not yet. An unrealized gain is an increase in the value of an asset that has not been sold.
Removal of the sale/purchase is often just the first in a series of consolidation entries necessitated by inventory transfers. Recognised in the accounts of the individual companies concerned, but; Profits made by members of a group on transactions with other group members are:
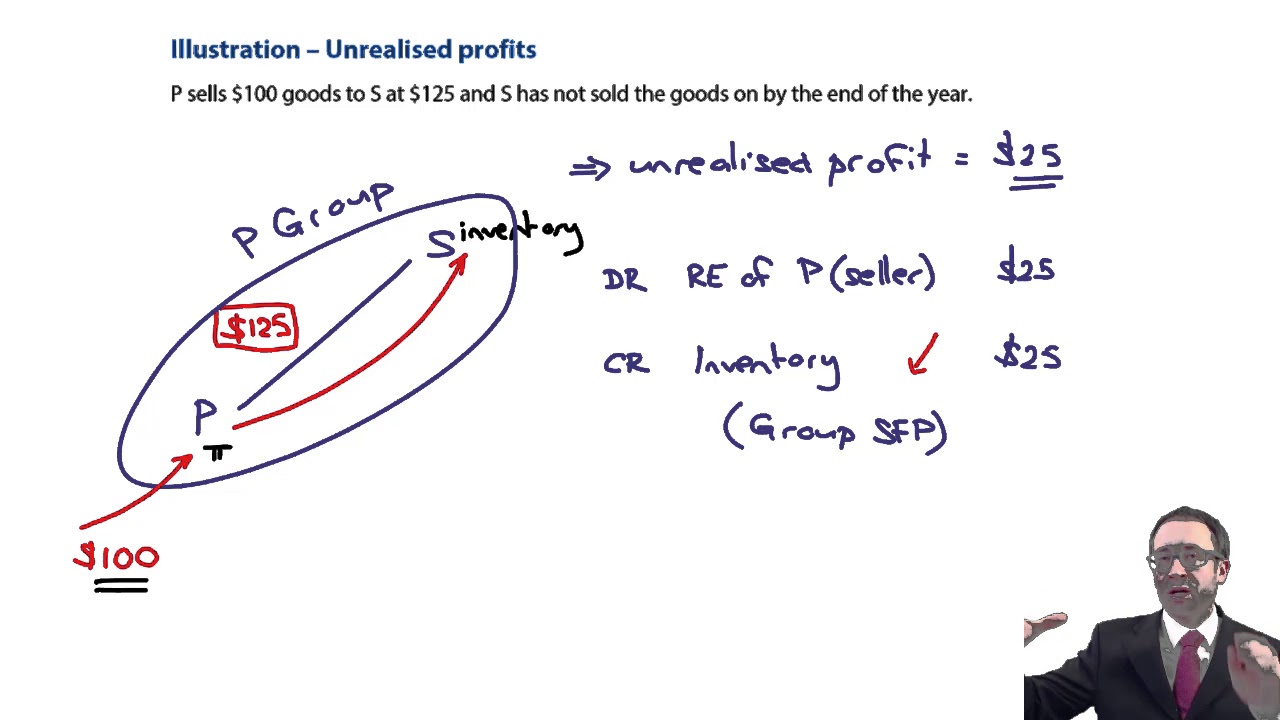
How do we then deal with unrealised profit if p buys goods for 100 and sells. It is, in essence, a paper profit. when an. Profits that were recognized before the investor acquired its interest in the investee, such as when inventories or other assets were sold by one company to another prior to the equity.
The unrealised profit is: Unrealized gross profit—year of transfer (year 1): Thus at 30 september 2007, the net.
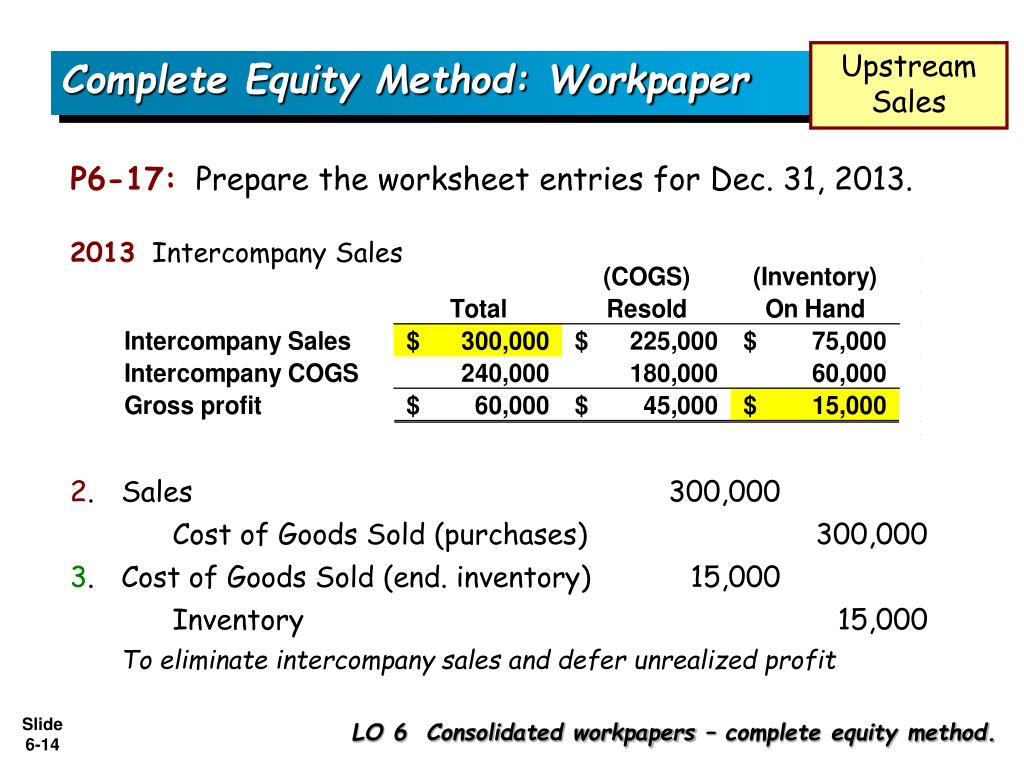
The accounting adjusting entries for nci require for those transactions which have the following. Adjustment for unrealised profit in inventory determine the value of closing inventory which has been purchased from the other company in the group. When one group company sells goods to another a number of adjustments may be needed.
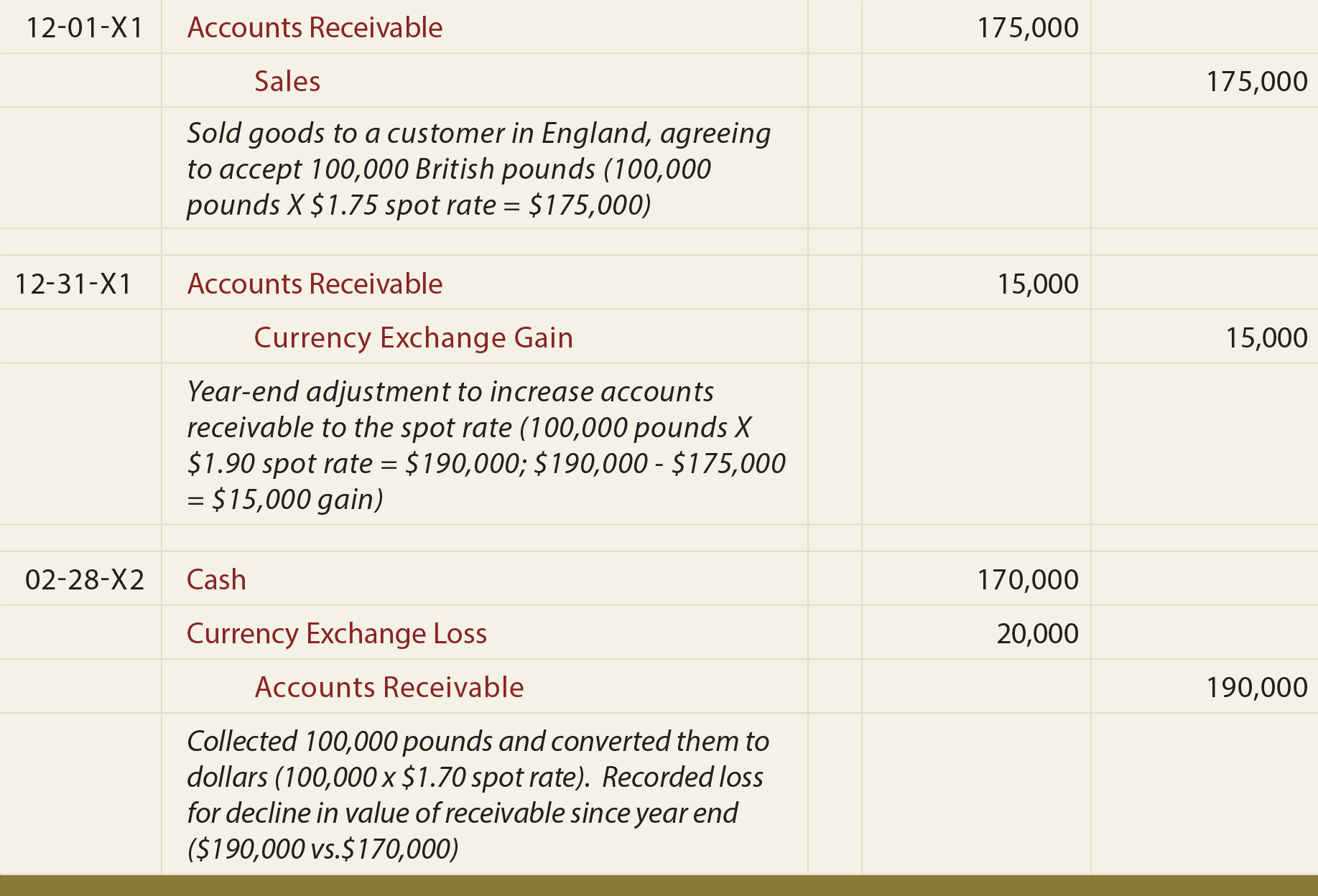
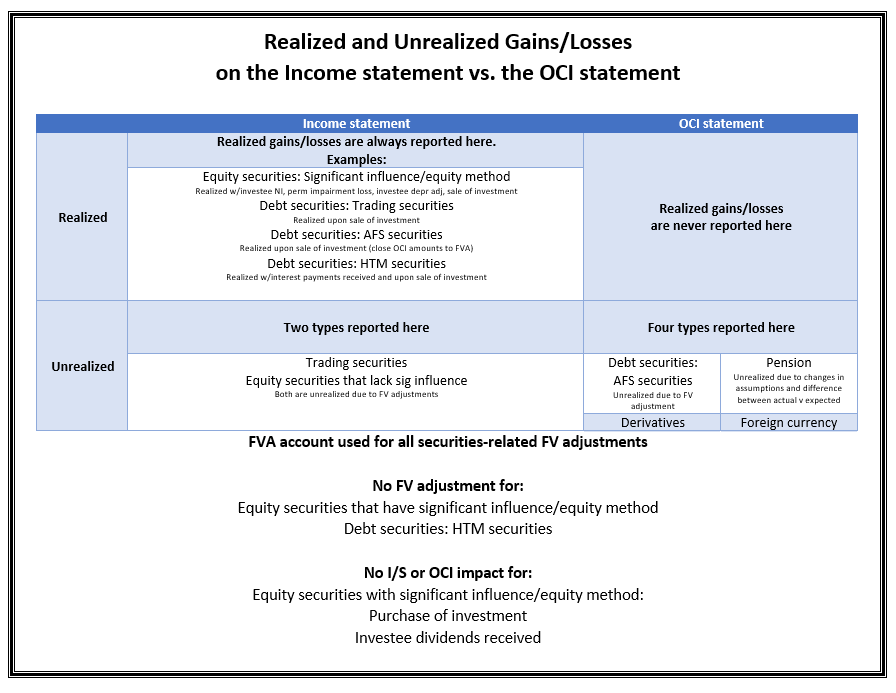
It means that the customer has already settled the invoice prior to the close of the. Unrealized gain is the increase of securities value while the company has not yet sold them. Unrealized gains or losses impact the “other comprehensive income” which is part of owner’s equity.
The second step here is to identify the provision for unrealised profit. When an investor purchase security, such as a stock, at one price and then sells it at a higher price, they have realized a gain. Until inventory is sold to entities outside the group, any profit is unrealised and should be eliminated from the consolidated financial statements.
For example, if you buy a stock for $10 and it rises to $15, you have an. Realized gains or losses are the gains or losses on transactions that have been completed. If the stock leaves the group it has become realised.
Profit between group companies 50 x 3/5 (what remains in stock) = 30. Equity securities are accounted for as a portfolio, and only one journal entry is made each reporting period that recognizes the net unrealized gain or loss on the. Adjustment journal entries, in a comprehensive case setting, should be prepared, using an examination question in the june 2016 session for illustration (see appendix).